Big-O Notation
Asymptotic Notations
| Name | Notation | Description | Simplified | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Big-O | O | Represents an (upper) bound on the growth rate of a function or the maximum resource consumption of an algorithm. | Order at Most <= | Associated with (worst-case) scenarios, indicating that the actual runtime will never exceed this upper limit. |
| Big-Theta | Θ | Represents a (tight) bound on the growth rate of a function or both the upper and lower bounds together. | Order Exactly == | Associated with (average-case) scenarios, indicating that the actual runtime will consistently fall within this bound. |
| Big-Omega | Ω | Represents a (lower) bound on the growth rate of a function or the minimum resource consumption of an algorithm. | Order at Least >= | Associated with (best-case) scenarios, indicating that the actual runtime will never exceed this lower limit. |
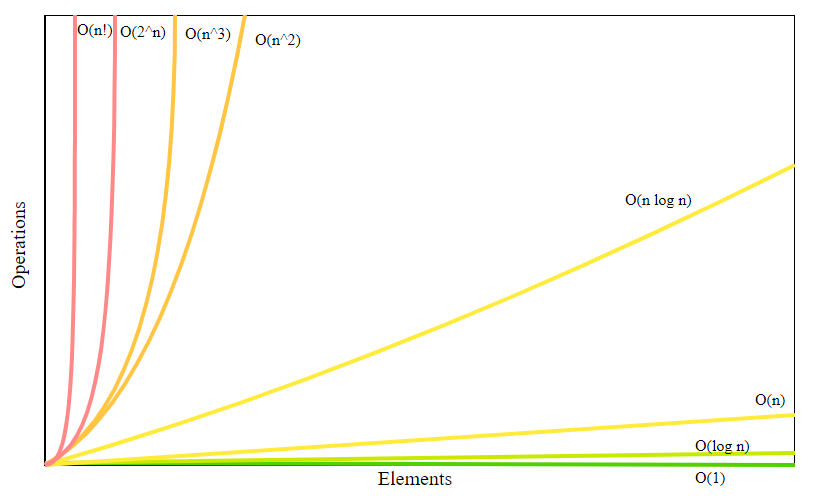
Time & Space Complexities
| Name | Notation | Description | Quality |
|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | O(1) | Constant time regardless of input size | Best |
| Logarithmic | O(log n) | Increases logarithmically with input size | Good |
| Linear | O(n) | Increases linearly with input size | Fair |
| Linearithmic | O(n log n) | Increases in proportion to the product of input size and its logarithm | Fair |
| Quadratic | O(n²) | Increases quadratically with input size | Bad |
| Cubic | O(n³) | Increases cubically with input size | Bad |
| Exponential | O(2ⁿ) | Doubles with each additional element in input | Worst |
| Factorial | O(n!) | Grows factorially with input size | Worst |
Complexity Chart
Important Notes
- Big-O (O), Big-Theta (Θ), and Big-Omega (Ω) are asymptotic notations, not the same as best, worst, and expected cases.
- When we say Log(n), we typically mean Log base 2.