| Array |  | List | A collection of elements, each identified by an index or a key | Θ(1) | Θ(n) | Θ(n) | Θ(n) | O(1) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) |
| Stack |  | List | Follows the Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) principle | Θ(n) | Θ(n) | Θ(1) | Θ(1) | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(1) | O(n) |
| Queue |  | List | Follows the First-In-First-Out (FIFO) principle | Θ(n) | Θ(n) | Θ(1) | Θ(1) | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(1) | O(n) |
| Single-Linked-List |  | List | Consists of nodes, each containing data and a reference to the next node. It allows efficient insertion and deletion at the head or tail | Θ(n) | Θ(n) | Θ(1) | Θ(1) | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(1) | O(n) |
| Double-Linked-List | 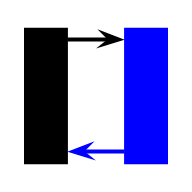 | List | Extends the single-linked list by having references to both the next and previous nodes. It enables bidirectional traversal | Θ(n) | Θ(n) | Θ(1) | Θ(1) | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(1) | O(n) |
| Skip-List | 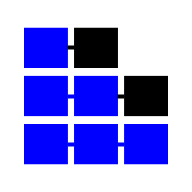 | List | Probabilistic data structure, it uses multiple levels of linked lists | Θ(log(n)) | Θ(log(n)) | Θ(log(n)) | Θ(log(n)) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n log(n)) |
| Binary-Search-Tree | 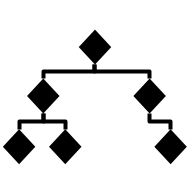 | Tree | Consists of nodes, each having at most two children | Θ(log(n)) | Θ(log(n)) | Θ(log(n)) | Θ(log(n)) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) |
| Cartesian-Tree | 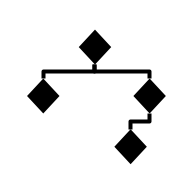 | Tree | Binary tree where the values of nodes satisfy the heap property with respect to both the parent and the child | N/A | Θ(log(n)) | Θ(log(n)) | Θ(log(n)) | N/A | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) |
| B-Tree | 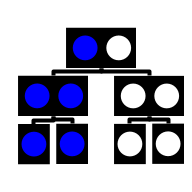 | Tree | Self-balancing tree structure that maintains sorted data and is commonly used in databases and file systems | Θ(log(n)) | Θ(log(n)) | Θ(log(n)) | Θ(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(n) |
| Red-Black-Tree | 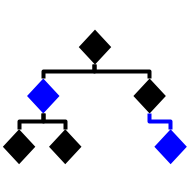 | Tree | Self-balancing binary search tree that maintains balance through color-coded nodes | Θ(log(n)) | Θ(log(n)) | Θ(log(n)) | Θ(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(n) |
| Splay-Tree | 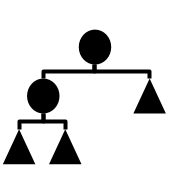 | Tree | Self-adjusting binary search tree. It reorganizes itself during operations to improve access times for frequently accessed nodes | N/A | Θ(log(n)) | Θ(log(n)) | Θ(log(n)) | N/A | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(n) |
| AVL-Tree |  | Tree | Self-balancing binary search tree. It ensures that the height difference between left and right subtrees is at most one | Θ(log(n)) | Θ(log(n)) | Θ(log(n)) | Θ(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(n) |
| KD-Tree | 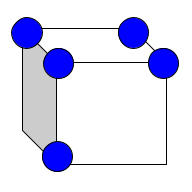 | Tree | Binary tree used for efficient multidimensional data search. It partitions space into regions based on data points | Θ(log(n)) | Θ(log(n)) | Θ(log(n)) | Θ(log(n)) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) |
| Min-Heap |  | Tree | The parent is less than or equal to its children | Θ(1) | Θ(n) | Θ(log(n)) | Θ(log(n)) | O(1) | O(n) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(n) |
| Max-Heap |  | Tree | The parent is greater than or equal to its children | Θ(1) | Θ(n) | Θ(log(n)) | Θ(log(n)) | O(1) | O(n) | O(log(n)) | O(log(n)) | O(n) |
| Hash-Table |  | Other | Uses a hash function to map keys to indices in an array | N/A | Θ(1) | Θ(1) | Θ(1) | N/A | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) |
| Graph |  | Other | Consists of nodes connected by edges | Θ(1) | Θ(V + E) | Θ(1) | Θ(1) | O(1) | O(V + E) | O(1) | O(1) | O(V + E) |
















